确认消息Confirm机制
消息确认,从前面的100%可靠性投递可以了解到,当生产者投递到Broker上时,如果开启了Confirm模式,会返回一个ACK给生产者,表示消息投递成功了。这也是消息可靠性投递的保障之一。
流程图
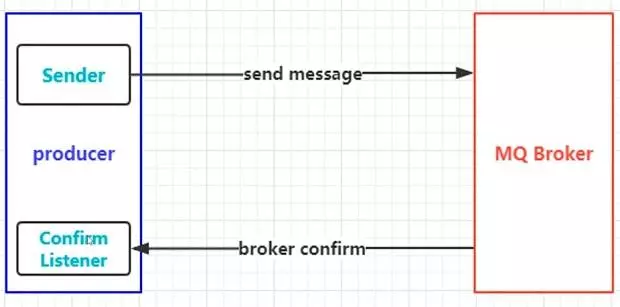
如图,消息生产者发送消息到MQ Broker上,Broker收到投递的消息并做出confirm响应。
生产者这里会配置一个Confirm Listener监听器,来监听confirm响应,因为操作是异步的,所以生产者将消息发送出去就可以做其他事情了,对于消息确认只需让内部监听器去监听即可。
代码实现Confirm
代码实现也很简单,主要在于Producer的代码修改,分为两步
- Channel信道开启confirm机制,
channel.confirmSelect() - 在Channel上添加监听器,
channel.addConfirmListener(ConfirmListener),并需实现ConfirmListener接口,重写成功和失败方法
生产端实现
1 | public class Producer { |
消费端实现
1 | public class Consumer { |
测试
先将Consumer启动后,查看15672可视化界面是否正确创建exchange,queue,以及binding
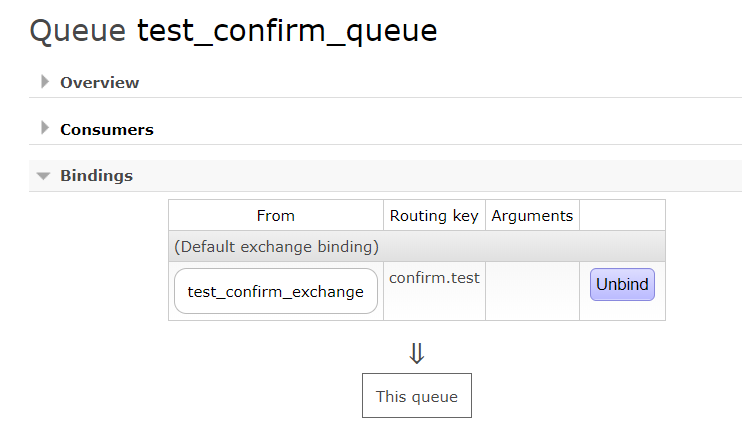
然后启动Producer,查看控制台
1 | - 消费者 |
正确打印结果
问题的提出
- 什么时候会走
handleNack方法呢
比如磁盘满了,MQ出现异常了,Queue容量上限了,等等
- 也有可能两个方法都不走
就是我们之前说的确认消息响应途中发生了网络闪断。
这种情况就需要定时任务去抓取中间状态的消息进行最大努力尝试次数的补偿重发,从而保障消息投递的可靠性。也就是我们之前说到的消息100%投递方案。
消息Return机制
在我们之前的学习中,所有的生产者将消息投递到MQ上时,RoutingKey都正确的将消息路由到Queue上,那么,有没有一种可能,就是RoutingKey设置错误,导致消息没有路由到Queue上,那么它会保存在Exchange上吗?
这时就需要Return机制了
- Return Listener用于处理消息不可达的状况
- 消息不可达指:没有对应的Exchange 或 指定的RoutingKey路由不到
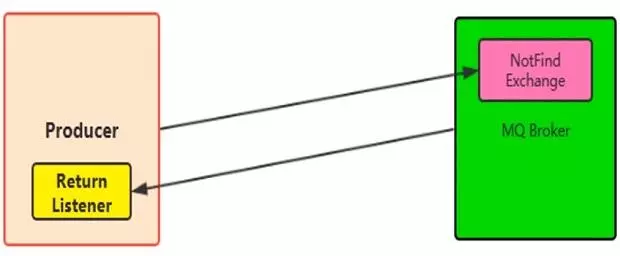
这两种情况下,就需要Return机制来处理不可达后的业务逻辑
Return机制实现
在代码中实现主要分为两步,当然也是在Producer端进行的
- 添加Return监听:
channel.addReturnListener(ReturnListener),和Confirm一样,添加一个监听器,并创建一个接口对其方法进行重写,这里的方法为handleReturn - 设置Mandatory属性:在发送消息的时候,有一个Mandatory参数
- 设置为true:开启Return机制,消息如果不可达,在MQ端会做出返回,由Return监听器监听
- 设置为false(默认):当消息不可达时,会自动删除此消息
Return代码实现
生产端实现
1 | public class Producer { |
消费端实现
消费者和之前代码一样,可写可不写
1 | public class Consumer { |
测试
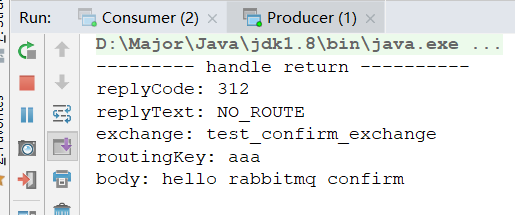
这里我们发送了错误的路由键,所以打印出返回的信息,这里响应信息为没有此路由,也应证说法。
如果我们使用正确的路由键,便会被正确消费,Producer不会有任何打印