一、SpringCloud CircuitBreaker
首先我们从SpringCloud的官方断路器注解@EnableCircuitBreaker入手
@EnableCircuitBreake
1 | (ElementType.TYPE) |
可以看到,真正有用的代码就是@Import那一行:
@Import(EnableCircuitBreakerImportSelector.class)
这里Import了一个选择器,是选择什么呢?就是这个断路器的实现类,即Hystrix
EnableCircuitBreakerImportSelector
1 | (Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 100) |
进入到断路器导入选择器中,可以看到代码很少,主要有两个重点
- 继承
SpringFactoryImportSelector父类,并且泛型为EnableCircuitBreaker - 可以在配置文件中通过
spring.cloud.circuit.breaker.enabled,进行断路器的开启和关闭
这样我们再进入SpringFactoryImportSelector
SpringFactoryImportSelector
1 |
|
代码较多,我们一点一点看
构造方法
首先看他的构造方法
1 | ("unchecked") |
这里主要是将注解类进行实例化,其实现,就是刚刚的那个泛型EnableCircuitBreaker
selectImport
然后我们再看selectImport方法,这个方法主要目的就是选择一个类,为我们的断路器实现类
1 |
|
1.获取注解类中的属性
1 | AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotationAttributes.fromMap( |
这里代码的意思就是将注解类里的注解信息进行保存
因为EnableCircuitBreaker中是空的,属性对于他来说不明显,这里我们换个类来解析下,比如@EnableCaching
1 | (ElementType.TYPE) |
这里可以看到有三个属性,对于AnnotationAttributes来说,是将这些属性保存在LinkedHashMap里的,其方法名为key,值为value,即proxyTargetClass为key,false为value
2.从spring.factories中加载自动配置类
1 | List<String> factories = new ArrayList<>(new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader |
这里可以看到SpringFactoriesLoader,即从META-INF/spring.factories中加载名称叫this.annotationClass,即EnableCircuitBreaker的自动配置类,这里我们可以全局搜一下EnableCircuitBreaker
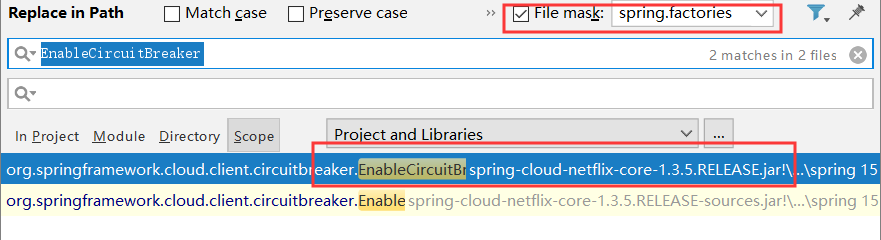
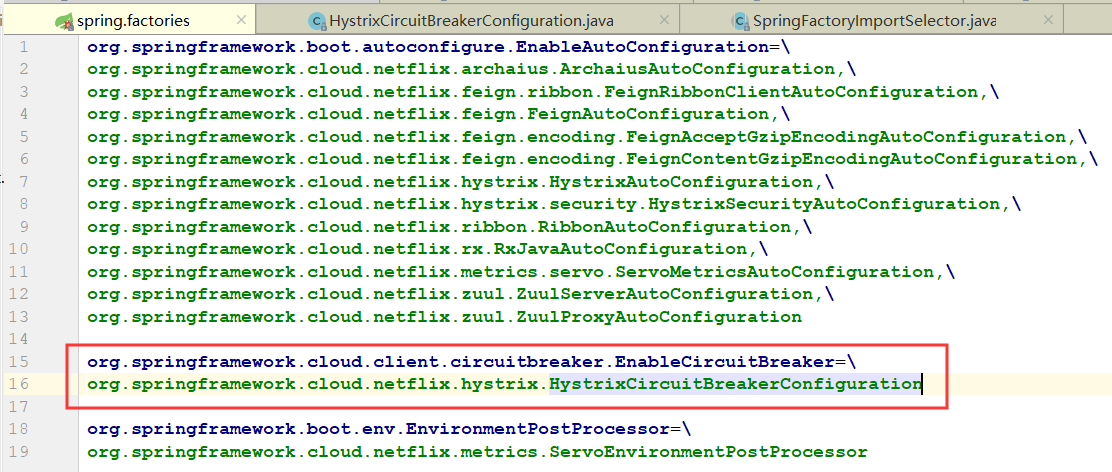
即会获取到HystrixCircuitBreakerConfiguration,这个自动配置类
3.返回数组
1 | return factories.toArray(new String[factories.size()]); |
将获取到的自动配置类集合转成数组返回
二、NetFlix Hystrix
我们接着HystrixCircuitBreakerConfiguration分析,因为接下来的源码都属于Hystrix包,所以另开了一个标题
HystrixCircuitBreakerConfiguration
在这个配置类中,有几个重要的组件
HystrixShutdownHook
1 | private class HystrixShutdownHook implements DisposableBean { |
这个组件主要功能是在Hystrix shutdown的时候,做一些清理工作
HystrixWebConfiguration
1 |
|
这个组件主要是开启Hystrix的Stream EndPoint,即可以访问/hystrix.stream来查看流信息,以及配合HystrixDashboard进行监控
HystrixMetricsPollerConfiguration
1 |
|
这个类是配置Hystrix的metrics指标,也不做过多介绍了
HystrixCommandAspect
Hystrix的命令切面,也是主要实现熔断的切面类,也是Hystrix最重要的类之一
1 |
|
在这个类中,首先可以看到两个切点
HystrixCommand:我们常用的配置熔断的注解HystrixCollapser:批量熔断的一个注解,不常用
接着往下看重要的方法methodsAnnotatedWithHystrixCommand()
1 | ("hystrixCommandAnnotationPointcut() || hystrixCollapserAnnotationPointcut()") |
我们一步步的分析:
切点拦截
1 | ("hystrixCommandAnnotationPointcut() || hystrixCollapserAnnotationPointcut()") |
这里,第一眼可以看到@Around中添加了上面所说的那两个切点,所以,当有方法添加了这两个注解时,便会被这个切面类拦截。
Method信息保存
1 | Method method = getMethodFromTarget(joinPoint); |
接着来到了这个方法,是获取被拦截方法的信息,保存到Method中。
MetaHolderFactory的初始化
1 | MetaHolderFactory metaHolderFactory = META_HOLDER_FACTORY_MAP.get(HystrixPointcutType.of(method)); |
再接着,是根据这个方法的Hystrix注解,判断是@HystrixCommand还是@HystrixCollapser来进行MetaHolderFactory的初始化,这里debug查看一下:
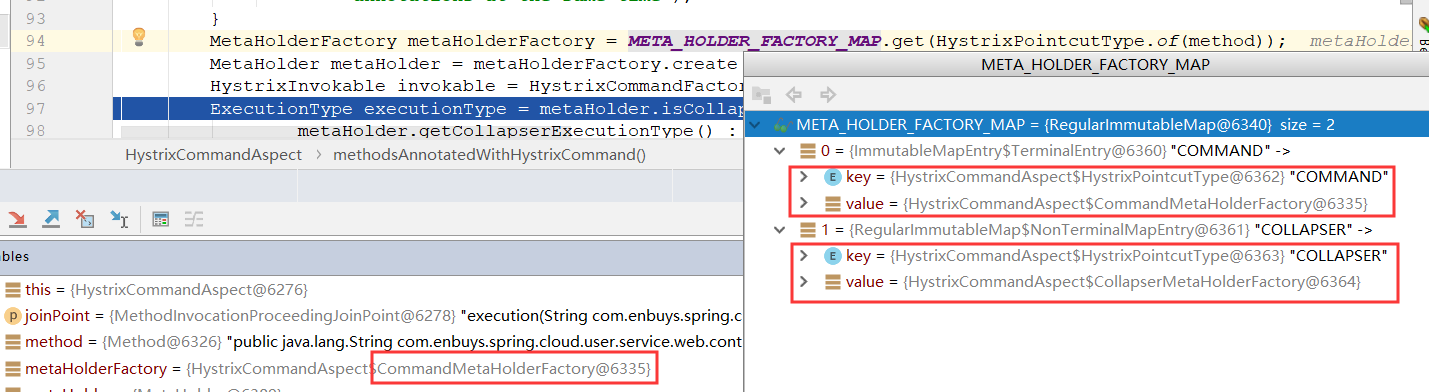
这里可以清楚的看到,因为方法上我们添加的是@HystrixCommand,所以工厂的实现是CommandMetaHolderFactory。
MetaHolder的实例化
1 | MetaHolder metaHolder = metaHolderFactory.create(joinPoint); |
这里可以看到,通过工厂创建了一个MetaHolder对象,对于此对象,保存的是方法信息,熔断设置等等。
比如方法名,返回值类型,熔断条件,fallback方法等,其实就是我们在那个类上设置的信息:

HystrixInvokable的实例化
1 | HystrixInvokable invokable = HystrixCommandFactory.getInstance().create(metaHolder); |
HystrixInvokable看名字,可以猜到是Hystrix熔断的可执行器,它本身是一个空方法,主要实现还是由下面的初始化来进行选择。
1 | public HystrixInvokable create(MetaHolder metaHolder) { |
这里有三个判断
- 对于
Collasper注解的使用CommandCollapser实现 - 对于实现了
isObservable,观察者模式的,使用GenericObservableCommand实现(属于RxJava的东西) - 其他情况,即普通情况,使用
GenericCommand,也是最常用的实现方法
所以,实际实现是由GenericCommand实现
这个类也很简单,就是对execute和fallback方法的执行做了实现,主要使用的是==反射==
方法的执行
最终来到最重要的一步,拦截方法的执行
1 | result = CommandExecutor.execute(invokable, executionType, metaHolder); |
进一步跟进
1 | public static Object execute(HystrixInvokable invokable, ExecutionType executionType, MetaHolder metaHolder) throws RuntimeException { |
这里可以看到,会判断是异步,同步 或者观察者模式的,进行不同的实现
常用的还是异步,即castToExecutable()方法,把HystrixInvokable转成HystrixExecutable,进而使用HystrixCommand的execute方法执行。
这里就不往下跟进了,实际就是使用了Future,异步多线程执行方法,也是在这里判断是否需要熔断的,真正触发的调用还是由GenericCommand完成。
总结
- 拦截标注
@HystrixCommand或@HystrixCollapser的方法(@Around) - 生成拦截⽅方法原信息,通过
MetaHolderFactory,对于不同的注解Command或Collasper,使用的工厂不同 - 生成
HystrixInvokable,通过HystrixCommandFactory,通过情况下由GenericCommand实现 - 执行方法,判断异步,同步或观察者模式,进行不同的转换
- 通过情况下,把
HystrixInvokable转成HystrixExecutable,进而使用HystrixCommand的execute方法执行。 - 最后通过
Future异步执行,判断是否需要熔断,最终方法的调用或者fallback方法的调用是由GenericCommand完成