一、Ribbon核心接口
对于下面介绍的接口,都很重要,他们组合在一起,就是负载均衡实现的原理,所以我们先来研究他们的接口,最后再看实现的步骤
1.负载均衡客户端
Spring对于命名非常灵性,对于负载均衡客户端,我们就可以在源码中搜索Load Balance Client即可,即可搜到LoadBalancerClient,即我们想要的接口,主要作用为:执行调用
LoadBalancerClient
这里我们简单放出源码,并进行一些转变,比如去掉注解,把父类的方法也拿进来之类的:
1 | public interface LoadBalancerClient extends ServiceInstanceChooser { |
这里主要有三个方法,我们先介绍下功能:
choose:选择服务器实例,通过一些负载算法,选定一台服务实例execute:请求执行回调,针对服务实例,执行具体的请求回调操作reconstructURI:转换URI,即把应用名称转换成IP加端口的具体路径,以方便请求
RibbonLoadBalancerClient
因为这里是接口,具体的实现还是要看实现类,对于Ribbon来说,实现类为RibbonLoadBalancerClient,我们进行源码查看,主要针对其实现方法:
reconstructURI
1 |
|
可以看到,这里做了一大堆的处理,主要目的是:将ServiceInstance中的实例信息转为Server对象保存,最后调用context.reconstructURIWithServer(server, uri);,所以具体的转换不在RibbonClient中,而是在RibbonLoadBalancerContext,所以我们后面在进行研究。
choose
1 |
|
通过源码不难看出,choose选择服务实例通过一层层递进,choose() -> getServer() -> getServer(loadBalancer) -> loadBalancer.chooseServer("default"),可以知道,最后使用的ILoadBalancer进行的实例选择,对于这个接口我们后面介绍。
对于execute方法是发出请求的重要方法,我们将所有接口都介绍完毕再进行解析。
2.负载均衡器上下文
Spring有他的ApplicationContext上下文,SpringCloud有BootstrapContext上下文,对于负载均衡器来说,也有他的上下文LoadBalancerContext,主要作用为:承上启下
LoadBalancerContext
主要职责:
- 转化 URI:将含应⽤用名称URI 转化成具体主机+端口的形式
- 组件关联:关联
RetryHandler、ILoadBalancer等 - 记录服务统计信息:记录请求相应时间、错误数量量等
默认实现:RibbonLoadBalancerContext,用于存储被负载均衡器使用的上下文内容以及API操作等等。
1 | public URI reconstructURIWithServer(Server server, URI original) { |
可以简单看下应用名与IP端口的转换,从reconstructURIWithServer的实现逻辑中,我们可以看到,它从Server对象中获取host和port信息,然后根据以服务名为host的URI对象original中获取其他请求信息,将两者内容进行拼接整合,形成最终要访问的服务实例的具体地址。
RibbonLoadBalancerContext
再看下实现类的源码:
1 | public class RibbonLoadBalancerContext extends LoadBalancerContext { |
可以看到,这里大量出现ILoadBalancer,这个就是我们的重头戏,负载均衡器!
3.负载均衡器
负载均衡器主要做用是维护服务器状态
ILoadBalancer
1 | public interface ILoadBalancer { |
具体的方法又:
addServers:添加服务实例chooseServer:通过关联的Key来获取服务实例或服务实例列表markServerDown:标记一个服务为DOWN状态,主要是由IPing的方式来检测,后面介绍getReachableServers:可用服务列表getAllServers:所有的服务列表
ZoneAwareLoadBalancer
接口的主要实现类,比如前面在RibbonLoadBalancerClient中的choose方法,就是使用的这个实现类的chooseServer
1 | public ZoneAwareLoadBalancer(IClientConfig clientConfig, IRule rule, |
这里可以看到,ILoadBalancer主要是维护服务器实例,对于真正选择一个实例的算法或者规则是rule.choose(key);这个方法,即IRule中的方法,所以我们下面介绍IRule
4.负载均衡规则接口
主要任务:在多个实例中根据规则选择一个实例
IRule
1 | public interface IRule{ |
这里主要方法就是choose,各种实现类对此方法进行重写,实现多种规则的实例选择,
实现IRule接口的首先是一个抽象类:
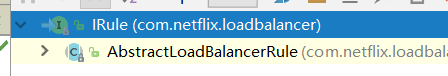
对于这个抽象类:
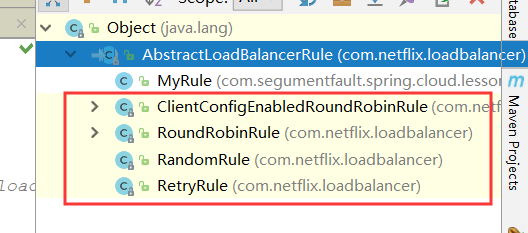
有很多官方实现的规则,比如RandomRule,随机选择,RoundRobinRule,轮询选择,而Ribbon对于默认的使用为ZoneAvoidanceRule,但是他没有重写choose方法,所以使用的是父类方法,我们看下他的组织结构:
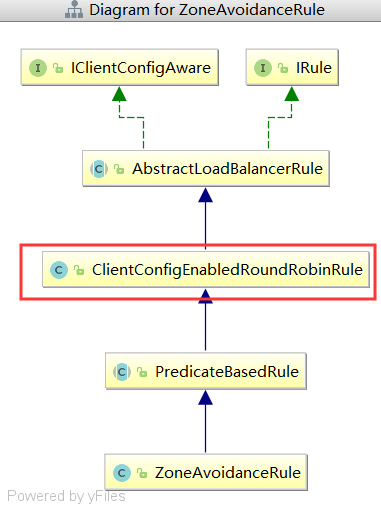
实际使用是ClientConfigEnabledRoundRobinRule
ClientConfigEnabledRoundRobinRule
1 |
|
这里实际使用的还是RoundRobinRule的choose方法,即轮询选择。
对于RoundRobinRule来说,也有很多子类:
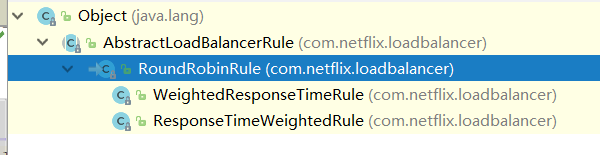
就不一一介绍了,我们只需知道IRule是负载均衡选择实例的规则即可`
5.Ping策略
主要任务:用来判断Server实例是否还存活
IPing
1 | public interface IPing { |
就一个主要方法,即根据指定服务器,检测是否存活
具体Ribbon使用的实现类为DummyPing
1 | public class DummyPing extends AbstractLoadBalancerPing { |
这里是永远返回true的
二、Ribbon负载均衡流程
有了前面的基础,现在我们一步步来分析Ribbon是如何实现负载均衡的。
首先我们做了哪些事?
- 向容器中添加
RestTemplate类,并添加@LoadBalanced注解 - 使用
restTemplate.postForObject()进行服务消费
1 |
|
首先我们debug进入postForObject方法
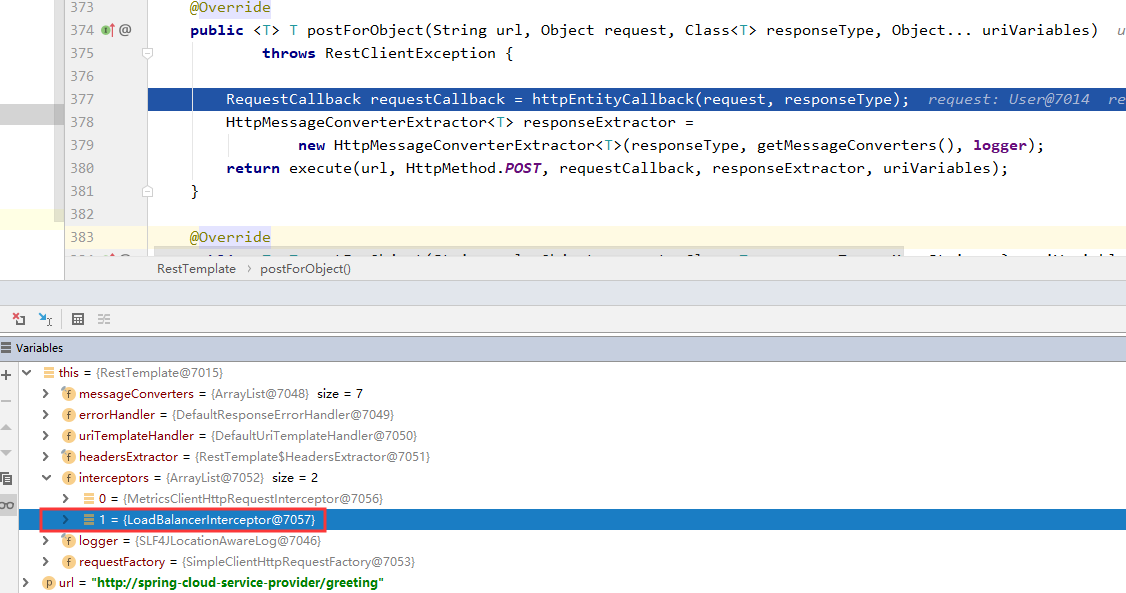
由上图可以明显的看到,有一个负载均衡拦截器LoadBalancerInterceptor
LoadBalancerInterceptor
1 |
|
可以明显的看懂,拦截后执行了LoadBalancer的execute方法,即RibbonLoadBalancerClient中的方法。
RibbonLoadBalancerClient
1 |
|
这里做了哪些事呢?
getLoadBalancer(serviceId):从上下文(RibbonLoadBalancerContext)中获取负载均衡器,即我们上面说的ZoneAwareLoadBalancer
getServer(loadBalancer):执行loadBalancer.chooseServer("default");方法,通过ZoneAwareLoadBalancer获取一个服务实例
所以我们下一步要进入到ZoneAwareLoadBalancer的chooseServer方法中
ZoneAwareLoadBalancer
这里其实就和上面1.3节介绍的一样啦,直接套用源码
1 | public ZoneAwareLoadBalancer(IClientConfig clientConfig, IRule rule, |
因为我们只有defaultZone,默认区域,所以直接请求父类chooseServer方法,在这里重要的方法是==rule.choose(key);==,即根据IRule规则接口选择一个可用的,这里具体的使用类为ZoneAvoidanceRule
ZoneAvoidanceRule
因为前面介绍过,这个类没有重写choose方法,所以实际使用还是父类ClientConfigEnabledRoundRobinRule的choose方法,即:
1 | public class ClientConfigEnabledRoundRobinRule extends AbstractLoadBalancerRule { |
进一步使用RoundRobinRule的轮询选择:
1 | public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) { |
这里省略了一些,可以自行去源码查看,只说比较重要的nextServerIndex,即可用的Server集合中的下一次选择索引,这样很简单的就实现了轮询。
可以发现,这里有个关键词 - 可用的Server集合,这里就和IPing有关了,实现类为DummyPing
DummyPing
这个Ping操作是定时去操作的,随便DummyPing是一定返回true,但是可以修改Ping,比如我们请求他的health端点,看看是否正确请求来判断他是否挂掉之类的。
回到RibbonLoadBalancerClient
接着我们回到RibbonLoadBalancerClient中的execute方法
1 |
|
经过上面一层层的调用执行,我们获取到了一个可用的Server实例,这里拿到要调用的服务的实例的后,把服务名,服务实例等信息包装到 RibbonServer对象中,然后执行重载的execute方法:
1 |
|
可以看到,这里执行了request.apply(serviceInstance);,即回调LoadBalancerInterceptor中的方法,我们再回到LoadBalancerInterceptor
回到LoadBalancerInterceptor
1 |
|
这里的回调方法即requestFactory.createRequest(request, body, execution),这里就不往深探索了,其实就是创建一个URIConnection,然后来调用远程服务~
总结
@LoadBalanced开启了RibbonLoadBalancerClient负载均衡支持- 当调用
RestTemplate发起请求时会被LoadBalancerInterceptor请求拦截器给拦截到 - 拦截器中使用了
RibbonLoadBalancerClient执行请求 - 然后根据服务id获取了负载均衡器,默认
ZoneAwareLoadBalancer - 然后负载均衡器进行服务的选择,默认使用
ZoneAvoidanceRule父类中的轮询策略 - 拿到服务实例后回调
LoadBalancerInterceptor中的requestFactory.createRequest()方法 - 最后使用
URIConnection完成服务调用请求,获取返回结果。
三、Ribbon自动配置
最后我们了解一下Ribbon的自动配置,就和SpringBoot一样,Ribbon也有他的自动配置类
RibbonAutoConfiguration
这个自动配置类主要是将LoadBalancerClient的实现改为RibbonLoadBalancerClient,源码如下:
1 |
|
这里还有一个小细节:@AutoConfigureAfter("....EurekaClientAutoConfiguration"),这里使用了After,是因为对于Ribbon来说,如果使用了Eureka,那么它的一些初始化实现会改变,比如ServerList的初始化
- 不使用Eureka:
ConfigurationBasedServerList - 使用Eureka:
DiscoveryEnabledNIWSServerList
其他最重要的就是对LoadBalancerClient的初始化,使他由RibbonLoadBalancerClient实现
LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration
1 |
|
这里源码已经很清晰了,当LoadBalancerAutoConfiguration加载时,会先对添加了@LoadBalanced注解的RestTemplate进行循环,通过RestTemplateCustomizer的customize添加拦截器LoadBalancerInterceptor。
这也是为什么当RestTemplate发出请求后,会被LoadBalancerInterceptor拦截的原因
RibbonClientConfiguration
这个自动配置类,是对Ribbon客户端进行自动配置,如下源码:
1 |
|
在这里可以应证我们第一节讲的LoadBalance核心接口的默认实现类,从上至下:
IRule——ZoneAvoidanceRuleIPing——DummyPingServerList——ConfigurationBasedServerList(如果有Eureka,使用DiscoveryEnabledNIWSServerList)ILoadBalancer——ZoneAwareLoadBalancerLoadBalancerContext——RibbonLoadBalancerContext