一、基础架构
Spring Cloud Eureke作为服务治理架构,有三个核心要素:
- 服务注册中心:Eureka Server,提供注册发现服务功能
- 服务提供方:Eureka Client,将自己的服务注册到注册中心,以供消费
- 服务消费方:消费者从注册中心获取服务,并且调用,实现方式有Ribbon或Fegin
下面我们详细说下从服务注册,到服务治理,到服务调用各个要素所涉及的重要通信行为
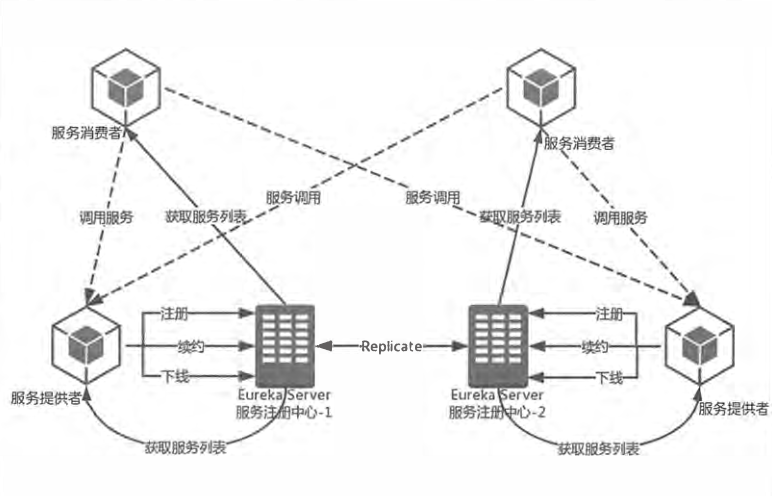
服务提供方
服务注册
服务提供者需要将自己的注册到Server,一般是通过REST请求,并携带自己独有的元信息,比如ip,端口,服务名等等。
服务注册需要开启配置:eureka.client.register-with-eureka=true(默认开启)
服务同步
注意,如图所示,有两个服务提供方分别到不同的注册中心注册,这时,因为注册中心高可用相互注册,所以当一个服务提供者注册时会请求转发到另一个注册中心,实现服务同步的功能。
服务续约
在服务注册完毕后,服务提供者会维护一个心跳,来告诉注册中心我还活着,防止注册中心的“失效剔除”将此服务排除。
服务续约有两个重要配置:
1 | # 用于定义心跳时间,默认30s续约一次 |
服务消费者
服务获取
当服务消费者获取服务时,会请求注册中心,注册中心为了性能考虑,会维护一份只读的服务列表副本,同时该缓存30秒更新一次。
获取服务必须开启配置:eureka.client.fetch-registry=true
修改缓存更新时间:eureka.client.registry-fetch-interval-seconds=30
服务调用
服务消费者获取清单后,根据返回的服务元数据信息,通过一些算法来进行服务调用,比如Ribbon使用轮询方式实现负载均衡的服务调用。
服务下线
在Client关闭时,会通过REST请求告知注册中心下线信息,注册中心会把服务状态改为DOWN,并传播给其他注册中心。
服务注册中心
失效剔除
当一段时间没有接收到客户端信息时,会将服务剔除,默认每隔60秒查询一次,如果有超过90秒没有续约的服务将被剔除
自我保护
当有些时候,查看Eureka图形化界面时,会发现一段话:
EMERGENCY! EUREKA MAY BE INCORRECTLY CLAIMING INSTANCES ARE UP WHEN THEY’RE NOT.
RENEWALS ARE LESSER THAN THRESHOLD AND HENCE THE INSTANCES ARE NOT BEING EXPIRED JUST
TO BE SAFE.
这是Eureka Server的自我保护机制,当Eureka Server运行期间,心跳失败比例在15分钟内低于85%,就会出现这个提示,将实力注册信息保护,不会过期,这个在单机调试时很经常出现。
本地开发时,添加配置来关闭自我保护eureka.server.enable-self-preservation=false
二、源码分析
我们通过一步步的源码,探究服务注册,获取,续约等实现
首先,我们知道Eureka Client非常简单,只需两步便可以将自己服务注册到Server上,即
- 开启注解
@EnableDiscoveryClient - 配置
eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone
我们根据这两点进行探寻,先进入注解查看
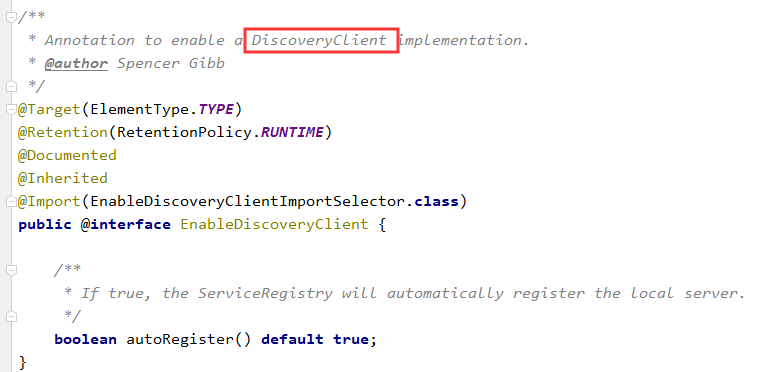
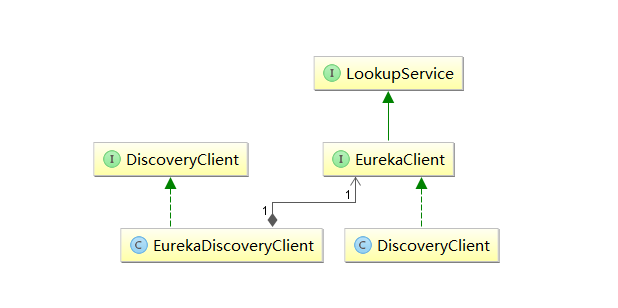
可以发现,非常简单,介绍中说是DisCoverClient的实现类,通过搜索DiscoveryClient,我们可以发现有一个类和一个接口。通过梳理可以得到如下图的关系:
主要的实现还是通过netflix的DiscoveryClient实现,我们进入查看;
首先源码非常多,我们先搜索serviceUrl试试
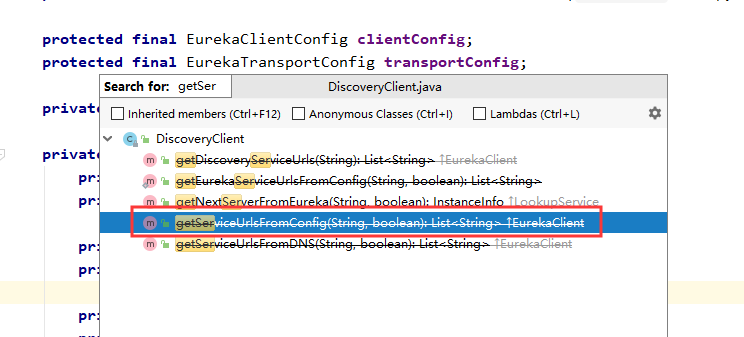
通过搜索发现一个过时方法,从配置中获取ServiceUrl,他是直接调用了EndpointUtils中的同名方法,如下:
1 | public static List<String> getServiceUrlsFromConfig(EurekaClientConfig clientConfig, String instanceZone, boolean preferSameZone) { |
Region、Zone
这里只放出我们需要的一些内容,如getRegion与getAvailabilityZones方法
getRegion:如果没有配置,默认去defaultRegion,一个Client只会有一个Region;可以通过配置eureka.client.region属性特殊定义getAvailabilityZones:如果没有配置,默认取defaultZone,由逗号分隔,可以有多个Zones,即Region与Zones是一对多关系,可以通过配置:eureka.client.availability-zones属性配置
ServiceUrl
紧接着可以看到,getEurekaServerServiceUrls()方法被调用了,用来获取ServiceUrls。
这个方法是由EurekaClientConfigBean实现的,这个方法在之前笔记中也有讲过:
1 |
|
做了几件事:
- 判断配置文件中是否修改了
defaultZone,比如叫DevZone - 如果不存在 使用默认的
defaultZone - 判断值是否存在,如果存在,将其转为String数组
- 循环添加到
eurekaServiceUrls这个List中,并返回
服务注册
看完这些必要的注册中心信息后,在回头查看NetFlix实现的DiscoveryClient类,来寻找服务注册的代码,
根据逻辑来说,服务注册,续约都是定时任务,应该找带有Scheduled的方法,查询一下
应该是这个initScheduledTasks():
1 | private void initScheduledTasks() { |
可以看到if (clientConfig.shouldRegisterWithEureka())这个条件,即注册服务,他实例化了一个InstanceInfoReplicator对象,应该是一个线程,进入看看它的run方法
1 | public void run() { |
可以看到,最重要的一行,就是discoveryClient.register();进入查看
1 | boolean register() throws Throwable { |
再进入查看eurekaTransport.registrationClient.register(instanceInfo);
找到EurekaHttpClientDecorator这个类,但是这个类是抽象类,我们需要找到它的子实现类
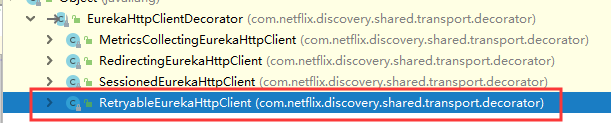
经过一一查看找到了RetryableEurekaHttpClient这个类,这个类发现了两个重要方法
- execut()
- getHostCandidates()
我们一一探索
1.execut()
1 |
|
因为代码长度过长,这里我们缩减一下:
1 | int endpointIdx = 0; |
在第10行,还有一个重要方法getHostCandidates(),我们也把源码贴出,一并查看
2.getHostCandidates()
1 | private List<EurekaEndpoint> getHostCandidates() { |
这里我们也精简一下:
1 | private List<EurekaEndpoint> getHostCandidates() { |
3.总结两个方法
getHostCandidates
- 先从配置文件中获取所有Zone配置
- 将这些信息与
quarantineSet集合中信息取交集,为不可用Eureka Server的集合 - 计算阈值
threshold(这个值很有用,后面会说到) - 判断是否第一次进入,如果是直接返回全部信息
- 判断不可用集合是否大于阈值,如果是清空Set,即返回空
- 最后的else进行添加,将可用的Server保存到List返回
execut
- 首先循环3次,这个次数是固定的,
DEFAULT_NUMBER_OF_RETRIES = 3; - 调用
getHostCandidates()方法获取可用的Eureka Server List - 获取完毕循环请求再此集合中的Server
- 如果成功,跳出返回
- 如果失败,
endpointIdx++,并将此Server保存到quarantineSet中,即不可用Eureka Server - 如果全部都失败,抛出异常
这里会有一个问题,我们一会再说
服务续约
1 | if (clientConfig.shouldRegisterWithEureka()) { |
从源码中,“服务续约”与“服务注册”在同一个if逻辑中,这个不难理解,服务注册到Eureka Server后,自然需要一个心跳去续约,防止被剔除,所以他们肯定是成对出现的。从源码中,我们可以清楚看到了,对于服务续约相关的时间控制参数:
1 | =30 |
而“服务获取”的逻辑在独立的一个if判断中,其判断依据就是我们之前所提到的eureka.client.fetch-registry=true参数,它默认是为true的,大部分情况下我们不需要关心。为了定期的更新客户端的服务清单,以保证服务访问的正确性。
这里看到服务续约为new HeartbeatThread(),
1 | private class HeartbeatThread implements Runnable { |
这里调用了renew方法
1 | boolean renew() { |
实现相对简单,直接以REST请求进行续约,如果续约失败,返回404会进行register,成功返回true并开始计时,等待下一次心跳
服务获取
紧接着,我们看看服务获取,这个实现也在刚刚看到的initScheduledTasks中,
1 | if (clientConfig.shouldFetchRegistry()) { |
if (clientConfig.shouldFetchRegistry())即我们之前开启的配置,其实他是默认开启的,eureka.client.fetch-registry=true
还可以发现getRegistryFetchIntervalSeconds()方法就是我们刚刚说的,修改缓存更新时间配置
因为源码相对复杂,就不细细探究了,主要会根据是否是第一次获取,来发起不同的REST请求和对应的处理,具体逻辑和之前类似。
注册中心注册
接下来我们看下注册中心是如何接收请求的, Eureka Server对于各类REST请求的定义都位于:com.netflix.eureka.resources包下。
在ApplicationResource中有一个addInstance()方法,应该是添加实例
1 |
|
这里可以发现,上面一大段都是判断实例的值是否存在等等,真正进行注册是registry.register(info, "true".equals(isReplication));调用了InstanceRegistry类的注册方法,如下:
1 |
|
这里我们之间查看父类register方法,对于handle看名字知道是对实例信息的处理:
1 | public void register(InstanceInfo registrant, int leaseDuration, boolean isReplication) { |
因为代码太长,我们精简一下,这里主要的注册就是将实例信息放ConcurrentHashMap中,即registry对象
1 | private final ConcurrentHashMap<String, Map<String, Lease<InstanceInfo>>> registry |
它是一个两层Map结构,第一层的key存储服务名:InstanceInfo中的appName属性,第二层的key存储实例名:InstanceInfo中的instanceId属性。
对于其他注册中心中的方法,都比较类似,就不一一查看了。
三、服务注册中的问题
因为默认只请求3次,那么比如我们的例子,有4个Server,前面三个都挂了,便不会再尝试8764了,直到下一次轮询请求连接Server。
这时因为不可用Set中已经保存了8761,8762,8763,所以,在我们的想法中,这一次请求会直接尝试8764,然后成功连接,然而这时错的,==它并不会走到这个分支,而是被上面的else if (quarantineSet.size() >= threshold)这个分支所拦截==,因为Set的容量为3,threshold是小于3的!
1 | else if (quarantineSet.size() >= threshold) { |
这时会把Set清空,那么再次循环请求的三次还是8761,8762,8763。并且再次注册失败!
那么,问题的关键是什么?
问题的关键就是threshold这个值的由来,因为此时quarantineSet.size()的值为3,而3这个值大于threshold,从而导致,会将quarantineSet集合清空,返回全量的Server列表。
threshold
1 | int threshold = (int) (candidateHosts.size() * transportConfig.getRetryableClientQuarantineRefreshPercentage()); |
先看代码,他是由配置的host数量乘以一个方法,我们看下这个方法:
1 | private double retryableClientQuarantineRefreshPercentage = 0.66D; |
可以看到,他是一个默认值,为0.66,所以4*0.66=2.64,所以3>2.64导致了这个问题,那么我们就应该尝试修改这个值,来达到我们的目的,在application.properties修改:
1 | =1 |
这样当判断是,阈值threshold=4,便会直接尝试注册8764了,如果是UP状态会成功连接,达到我们想要的效果